Testosterone All you need to know
“Unlock vitality naturally! Explore the comprehensive guide to optimize testosterone levels, navigate age-related changes, and embrace lifestyle strategies for holistic well-being.”
Understanding Testosterone
Testosterone, a hormone primarily associated with masculinity, plays a pivotal role in various physiological functions. It is produced in the testicles (and in smaller amounts in the ovaries for females) and is essential for the development of male reproductive tissues
The Natural Essence of Testosterone
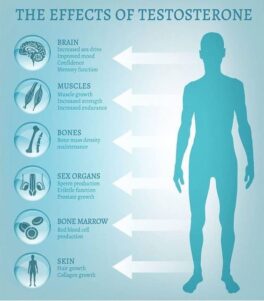
In the intricate realm of human biology, the natural essence of testosterone emerges as a cornerstone of vitality. This hormone, crafted by the body’s inner alchemy, plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance necessary for optimal health.
Testosterone is, fundamentally, a naturally occurring hormone, and its origins lie within the endocrine system. In males, the testicles take on the responsibility of testosterone production, while in females, the ovaries contribute smaller amounts. This natural synthesis reflects the body’s inherent wisdom in orchestrating hormonal harmony.
Embracing Nature’s Blueprint
Nature, in its infinite wisdom, has woven testosterone into the very fabric of human existence. This hormone is not an external elixir but a product of the body’s intricate dance of biological processes. It is a testament to the marvel of evolution, ensuring that each individual, regardless of gender, is endowed with the biological essence needed for various physiological functions.
Testosterone and Reproductive Vitality
The natural essence of testosterone finds its pinnacle in the realms of reproduction. In males, this hormone plays a pivotal role in the development of the testicles, influencing the maturation of sperm and fostering reproductive vitality. Beyond reproduction, testosterone contributes significantly to the maintenance of muscle mass and bone density, underlining its multifaceted importance.
Hormonal Symphony of Life
The natural synthesis of testosterone is not a solitary act but a part of a grand hormonal symphony orchestrated by the endocrine system. It operates in concert with other hormones, ensuring a harmonious balance that is essential for overall well-being.
Suggestions : Do Onion Increase Testosterone level
Unraveling the Role of Testosterone

Delving into the intricate landscape of human physiology, testosterone emerges as a multifaceted hormone, unraveling its role in shaping various aspects of our health and well-being.
- The Key Player in Libido and Sexual Function
At the forefront of testosterone’s role lies its influence on libido and sexual function. This hormone acts as a potent catalyst, igniting the flames of desire and steering the intricate dance of reproductive processes. It stimulates the production of sperm, ensuring fertility and contributing to the vitality of human reproduction.
- Muscle Mass and Bone Density Maintenance
Beyond its pivotal role in reproduction, testosterone assumes the mantle of a guardian, actively participating in the maintenance of muscle mass and bone density. It serves as a sculptor of the body’s structural framework, fostering the development of robust muscles and promoting the integrity of the skeletal system.
- Cognitive Function and Emotional Well-being
Testosterone extends its influence beyond the physical realm, making significant contributions to cognitive function and emotional well-being. Research suggests that optimal testosterone levels are associated with improved mood, cognitive sharpness, and overall mental well-being. The hormone acts as a modulator, influencing aspects of memory, focus, and emotional resilience.
- Metabolic Regulation and Fat Distribution
In the intricate symphony of metabolic processes, testosterone plays a vital role in regulating metabolism and influencing fat distribution. Balanced testosterone levels contribute to the efficient distribution of fat, preventing disproportionate accumulation and promoting a healthier body composition.
- Erythropoiesis and Red Blood Cell Production
Testosterone’s influence extends to the realm of blood production, specifically erythropoiesis—the process of red blood cell formation. Adequate testosterone levels contribute to the regulation of red blood cell production, supporting oxygen transport and overall cardiovascular health.
- Energy Levels and Physical Performance
As a natural energizer, testosterone enhances energy levels and physical performance. It acts as a motivator for physical activity, contributing to the stamina and endurance needed for an active lifestyle.
The Intricate Workings of Testosterone
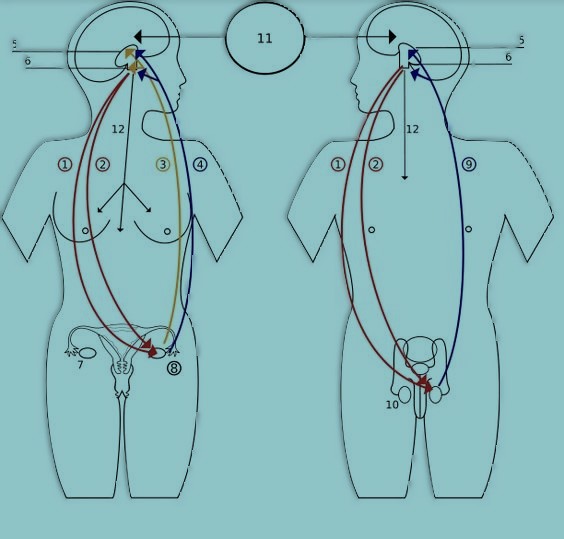
As we journey into the biological tapestry of human health, the workings of testosterone unfold as an intricate dance of hormones and cellular signaling, shaping fundamental aspects of our physiology.
- Hormonal Regulation
At the heart of testosterone’s workings lies a finely tuned system of hormonal regulation. The hypothalamus, a region of the brain, releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), signaling the pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This orchestration ensures the stimulation of testosterone production in the testes.
- Cellular Receptors and Signaling
The influence of testosterone extends to the cellular level, where it interacts with androgen receptors on target cells. This binding initiates a cascade of intracellular events, including the activation of specific genes and the modulation of cellular functions. The intricate dance of cellular signaling ensures that testosterone’s effects are precisely calibrated to meet the body’s needs.
- Feedback Mechanisms
The body maintains a delicate balance in testosterone levels through feedback mechanisms. As testosterone levels rise, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland receive signals to reduce the release of GnRH, LH, and FSH, creating a self-regulating loop. Conversely, when testosterone levels dip, these signals increase, stimulating the production of testosterone to restore equilibrium.
- Conversion of Testosterone to Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and Estradiol
Testosterone undergoes conversion to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and estradiol through enzymatic processes. DHT plays a crucial role in the development of male characteristics, including the growth of facial hair and the deepening of the voice. Estradiol, a form of estrogen, is essential for bone health and other physiological functions.
- Transportation in the Bloodstream
Testosterone, once synthesized, travels through the bloodstream bound to proteins. This transportation mode ensures the hormone reaches its target tissues and cells, where it can exert its effects.
- Metabolism and Excretion
The body metabolizes testosterone, and the metabolites are eventually excreted through urine. Understanding the metabolism and excretion of testosterone provides insights into the dynamic life cycle of this hormone within the body.
- Circadian Rhythms and Testosterone Production
Testosterone production follows a circadian rhythm, with levels peaking in the early morning and declining throughout the day. This natural fluctuation reflects the intricate interplay between hormonal regulation and the body’s internal clock.
Reaping the Benefits of Adequate Testosterone
Optimal levels of testosterone offer a plethora of benefits that extend far beyond its association with masculinity. Let’s explore the diverse advantages that come with maintaining a balanced and healthy testosterone profile.
- Enhanced Libido and Sexual Function
Adequate testosterone levels play a pivotal role in fostering a healthy libido and supporting optimal sexual function. This hormone is a key player in stimulating the production of sperm, ensuring reproductive vitality and contributing to a satisfying sex life.
- Improved Mood and Cognitive Function
Testosterone’s influence reaches beyond the physical realm, making significant contributions to mental well-being. Research suggests that optimal testosterone levels are associated with improved mood, reduced irritability, and enhanced cognitive function. A balanced hormonal profile can positively impact memory, focus, and overall mental clarity.
- Increased Muscle Mass and Strength
One of the most recognized benefits of testosterone is its impact on muscle development. Adequate levels of testosterone contribute to the growth and maintenance of lean muscle mass, fostering increased strength and physical performance. This aspect is particularly relevant for individuals engaged in resistance training and exercise.
- Healthy Bone Density
Testosterone plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy bone density. It contributes to the development and strength of bones, reducing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis, especially as individuals age. Adequate testosterone levels are essential for skeletal integrity and overall musculoskeletal health.
- Efficient Fat Distribution
Balanced testosterone levels contribute to optimal fat distribution in the body. This hormonal balance helps prevent the disproportionate accumulation of body fat, promoting a healthier body composition. This is particularly relevant for metabolic health and the prevention of obesity-related conditions.
- Regulation of Red Blood Cell Production
Testosterone’s influence extends to the production of red blood cells, a process known as erythropoiesis. This regulation ensures a sufficient supply of oxygen-carrying red blood cells, supporting cardiovascular health and overall vitality.
- Increased Energy Levels
As a natural energizer, testosterone contributes to increased energy levels and overall vitality. Individuals with optimal testosterone levels often report higher levels of motivation, stamina, and endurance, supporting an active and engaged lifestyle.
- Improved Metabolic Health
Balanced testosterone levels are associated with improved metabolic health. This includes better insulin sensitivity, glucose regulation, and lipid profiles. Maintaining hormonal balance contributes to a reduced risk of metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes
Age and Its Impact on Testosterone Levels
A fundamental aspect of the testosterone narrative unfolds as we explore the dynamic interplay between age and hormonal fluctuations. Understanding how the passage of time influences testosterone levels provides crucial insights into the challenges and opportunities for maintaining optimal health.
- Understanding Age-Related Decline
As individuals embark on the journey of aging, a natural and gradual decline in testosterone levels occurs. This phenomenon, often referred to as andropause in men, typically begins around the age of 30. The rate of decline varies among individuals, but on average, testosterone levels may decrease by approximately 1% per year.
- Physiological Changes and Symptoms
The age-related decline in testosterone is accompanied by various physiological changes that can manifest as symptoms. These may include reduced energy levels, diminished muscle mass, increased body fat, changes in mood, and a decline in sexual drive. While these changes are part of the natural aging process, maintaining optimal testosterone levels becomes a key consideration for overall well-being.
- Impact on Reproductive Health
Testosterone’s role in reproductive health becomes particularly pronounced with age. While it is a natural part of the aging process for fertility to decrease, suboptimal testosterone levels can exacerbate this decline. Addressing age-related changes in testosterone becomes essential for those considering family planning later in life.
- Cognitive Function and Aging
Research suggests a potential link between testosterone levels and cognitive function in aging individuals. While more studies are needed to establish a clear connection, maintaining balanced testosterone levels may contribute to cognitive sharpness and help mitigate age-related cognitive decline.
- Cardiovascular Health Concerns
Age-related changes in testosterone levels may also impact cardiovascular health. Low testosterone has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular issues, including atherosclerosis and heart disease. Managing testosterone levels becomes a factor in a holistic approach to cardiovascular well-being.
- Addressing Age-Related Challenges
While age-related decline in testosterone is inevitable, adopting a proactive approach to mitigate its impact is crucial. Lifestyle factors play a significant role in maintaining hormonal balance. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and stress management contribute to overall well-being and may positively influence testosterone levels.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy Considerations
For some individuals experiencing significant symptoms of low testosterone, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be a consideration. However, the decision to pursue HRT should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional, weighing the potential benefits against the associated risks.
Naturally Boosting Testosterone

Amidst the evolving landscape of health and wellness, the quest for naturally boosting testosterone takes center stage. Empowering individuals to optimize hormonal balance through lifestyle choices becomes a pivotal aspect of fostering overall well-being.
- Exercise and Resistance Training
Engaging in regular physical activity, particularly resistance training, emerges as a potent catalyst for boosting testosterone levels naturally. Resistance exercises, such as weightlifting, trigger the release of growth hormone and stimulate the production of testosterone. Incorporating a well-rounded exercise routine into daily life contributes not only to hormonal balance but also to overall fitness.
- Nutritional Strategies
A balanced and nutrient-rich diet plays a pivotal role in supporting optimal testosterone levels. Specific nutrients, such as zinc and vitamin D, are crucial for testosterone synthesis. Including foods like lean meats, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens in the diet provides essential building blocks for hormone production. Dietary choices that prioritize whole foods and minimize processed sugars contribute to overall metabolic health, further supporting hormonal balance.
- Adequate Sleep and Stress Management
Quality sleep and effective stress management are integral components of natural testosterone optimization. Lack of sleep and chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which, in turn, may suppress testosterone production. Prioritizing a consistent sleep schedule and adopting stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, contribute to hormonal equilibrium.
- Maintaining a Healthy Body Weight
Achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight is linked to optimal testosterone levels. Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, is associated with increased estrogen production and lower testosterone levels. Embracing a lifestyle that includes regular physical activity and a balanced diet supports both weight management and hormonal balance.
- Limiting Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption has been linked to reduced testosterone levels. Moderation in alcohol intake, or choosing to abstain, supports hormonal health. Alcohol can interfere with the endocrine system, impacting the synthesis and regulation of hormones, including testosterone.
- Sun Exposure for Vitamin D
Vitamin D, synthesized in the skin through exposure to sunlight, plays a crucial role in testosterone production. Ensuring adequate sun exposure or considering vitamin D supplementation, especially in regions with limited sunlight, supports overall health and hormonal balance.
- Avoiding Endocrine Disruptors
Limiting exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals, commonly found in certain plastics and environmental pollutants, is essential for hormonal health. These substances can interfere with the body’s hormonal regulation, including testosterone production.
- Hydration and General Lifestyle Choices
Staying well-hydrated and adopting a generally healthy lifestyle contribute to maintaining hormonal balance. Hydration supports overall bodily functions, including those related to hormone synthesis and regulation. Avoiding tobacco and minimizing exposure to environmental toxins further aligns with a holistic approach to hormonal well-being.
Conclusion
In our exploration of testosterone, we’ve unveiled its natural essence, role, intricate workings, benefits, and the impact of age. Understanding the interplay of these factors is crucial for holistic well-being. As age influences testosterone levels, proactive lifestyle choices become pivotal. The benefits of optimal testosterone, from enhanced libido to improved metabolic health, underscore its significance. Moreover, natural strategies, including exercise, nutrition, and stress management, empower individuals to maintain hormonal balance naturally. This journey toward comprehensive health encapsulates the essence of testosterone and its profound impact on the vibrant tapestry of life.